Topic Modelling Meets Deep Neural Networks: A Survey (arXiv , 2021)
Abstract
A focused yet comprehensive overview of neural topic models for interested researchers in the AI community, so as to facilitate them to navigate and innovate in this fastgrowing research area.
To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first review focusing on this specific topic.
Introduction
- Bayesian probabilistic topic models (BPTMs) have been the most popular and successful series of models with LDA
- A BPTM usually specifies a probabilistic generative model
- Like other Bayesian models, the learning of a BPTM is done by a (Bayesian) inference process
e.g) variational inference (VI) and Monte Carlo Markov Chain sampling
- Topic Modeling with big data and deep learning
1) Given a specific BPTM, Unfortunately, it is also hard to automate the design of the inference processes.
2) With the recent developments in DNNs and deep generative models, there has been an emerging research direction which aims to leverage DNNs to boost performance, efficiency, and usability of topic modelling, named neural topic models (NTMs)
- In this paper, we would like to fill this gap by providing an overview for interested researchers who want to develop new NTMs and/or to apply NTMs in their domains.
- The Contributions of this survey
1) We propose a taxonomy of NTMs where we categorise existing models based on their backbone framework.
2) We first provide an informative discussion and overview of the background and evaluation methods for NTMs
3) Conduct a focused yet comprehensive review, offering detailed comparisons of the variants in different categories of NTMs with applications.
4) We identify the limitations of existing methods and analyse the possible future research directions for NTMs.
Background , Definitioin and Evaluation
2.1 Background and Definition
The 3 point of Topic Modeling : document, word, and topic
NTM process : [Data -> Latent Variable -> Learning] or [Data -> Embedding -> Input -> Latent Variable -> Learning]
- Notations
D, Z, and T to denote the corpus with
D : all the document data,
Z : The collections of topic distributions of all the documents
T : The collections of word distributions of all the topics
- Summary of Topic Generative Process
주어진 Data 를 latent space 로 projection -> using sampled prior distribution -> inference process -> posterior distribution
For NTMs, these probabilities are typically parameterised by deep neural networks.
2.2 Evaluation
Predictive Accuracy
A more popular metric based on log-likelihood is perplexity
issues :
1) As topic models are not for predicting unseen data but learning interpretable topics and representations of seen data, predictive accuracy does not reflect the main use of topic models.
2) Predictive accuracy does not capture topic quality.
Predictive accuracy and human judgement on topic quality are often not correlated [7], and even sometimes slightly anti-correlated.
3) The estimation of the predictive probability is usually intractable for Bayesian models and different papers may apply different sampling or approximation techniques.
For NTMs, the computation of log-likelihood is even more inconsistent, making it harder to compare the results across different papers.
Topic Coherence
Experiments show topic coherence (TC) computed with the coherence between a topic’s most representative words (e.g, top 10 words) is inline with human evaluation of topic interpretability [32].
Various formulations have been proposed to compute TC, we refer readers to [49] for more details.
Most formulations require to compute the general coherence between two words, which are estimated based on word co-occurrence counts in a reference corpus.
Regarding TC :
1) The ranking of TC scores may vary under different formulations.
Therefore, it is encouraged to report TC scores of different formulations or report the average score.
2) The choice of the reference corpus can also affect the TC scores, due to the change of lexical usage, i.e, the shift of word distribution.
For example, computing TC for a machine learning paper collection with a tweet dataset as reference may generate inaccurate results.
Popular choices of the reference corpus are the target corpus itself or an external corpus such as a large dump of Wikipedia.
3) To exclude less interpretable “background” topics, one can select the topics (e.g., top 50%) with the highest TC and report the average score over those selected topics [69] or to vary the proportion of the selected topics (e.g, from 10% to 100%) and plot TC score at each proportion [70].
Topic Diversity
Topic diversity (TD), as its name implies, measures how diverse the discovered topics are.
It is preferable that the topics discovered by a model describe different semantic topical meanings.
Specifically, [11] defines topic diversity to be the percentage of unique words in the top 25 words
Neural Topic Models with Amortised Variational Inference
Recently , Using Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) and amortised variational inference (AVI) + BPTMs
=> This series of models VAE-NTMs
- The generation process of VAE
A VAE model by maximising the Evidence Lower BOund (ELBO) of the marginal likelihood of the BoW data b in terms of θ, φ, and T : Ez∼q z [log p(b | z)] − KL[q z k p z ] , where the RHS term is the Kullback-Leiber (KL) divergence.
To compute/estimate gradients, tricks like reparameterisations are usually used to back-propagate gradients through the expectation in the LHS term and approximations are applied when the analytical form of the KL divergence is unavailable.
- To adapt the VAE framework for topic modelling, there are two key questions to be answered:
1) Different from other applications, the input data of topic modelling has its unique properties, i.e., b is a high-dimensional, sparse, count-valued vector and s is a variable-length sequential data.
How to deal with such data is the first question for designing a VAE topic model.
2) Interpretability of topics is extremely important in topic modelling.
토픽모델링에서 생성된 토픽의 해석가능성은 매우 중요하다.
When it comes to a VAE model,
How to explicitly or implicitly incorporate the word distributions of topics (i.e., T ) to interpret the latent representations or each dimension remains another question
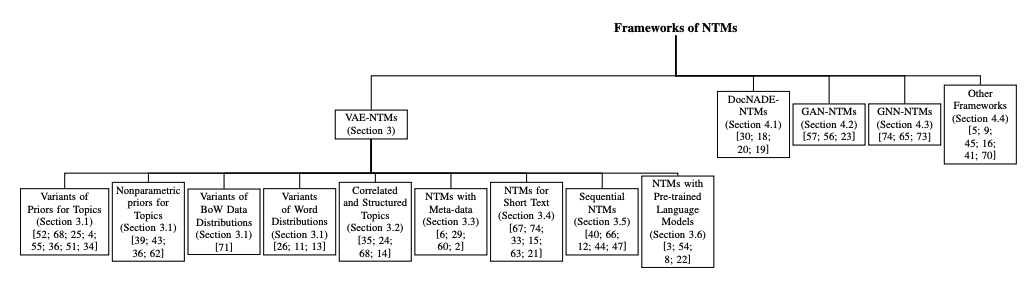
3.1 Variants of Distributions
Given the knowledge and experience of BPTMs, z’s prior plays an important role in the quality of topics and document representations in topic models.
Thus, various constructions of the prior distributions and their corresponding posterior distributions have been proposed for VAE-NTMs, aiming to be better alternatives to the normal distributions used in the original model
Variants of Prior Distributions for z
Dirichlet 분포를 Variational Autoencoder Neural Topic Models (VAE-NTMs)에 통합하는 데 접근 방법에 대해 다룹니다.
- LDA 및 VAE-NTMs에서의 Dirichlet 분포
- Dirichlet 분포는 Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)에서 주제의 부드러움과 희소성을 촉진하기 위해 사용
- 그러나 Dirichlet에 대한 효과적인 재매개화 함수 (RF) 부재로 ELBO의 기대값의 기울기를 계산하는 것이 어렵다
- Dirichlet 분포 근사치의 시도
- 도전을 해결하기 위해 다양한 근사치가 제안되었습니다
- Laplace 근사: Dirichlet 샘플을 로지스틱 정규 분포에서 샘플을 사용하여 근사화
- Weibull 분포: Dirichlet 분포를 시뮬레이션하는 데 사용되는 감마 변수의 근사치로 제안
- 누적 분포 함수 근사치: 감마의 거부 샘플러의 제안 함수를 감마 분포의 RF로 사용하여 감마의 누적 분포 함수를 근사화
- Rounded RF: Dirichlet 샘플을 둥근 사후 분포에서 뽑아 근사화
- VAE-NTMs에서의 다른 분포 접근 방법
- Gaussian softmax (GSM) 함수: 인코더에 도입함
- 로지스틱-정규 혼합 분포: \(z\)의 사전 분포로 제안됩니다.
- Sparsemax 함수: \(z\)의 희소성을 강화하기 위해 \(G\)에서 softmax 함수를 대체하기 위해 도입됩니다.
- RF가 없는 분포에 대한 일반적인 접근 방법
- RF가 없는 분포에 대한 일반적인 접근 방법은 VAE-NTMs에서 적용 가능하며, [50; 38]에서 논의된 것과 같이 사용
- Dirichlet 이외의 선택지
- Gaussian softmax (GSM) 함수 및 로지스틱-정규 혼합 분포는 인코더 prior 의 Dirichlet의 대안으로 소개
요약하면, 이 텍스트는 VAE-NTMs에서 Dirichlet 분포와 관련된 도전, 이러한 도전을 극복하기 위한 다양한 근사치, 그리고 주제 모델링 및 VAE 컨텍스트에서 latent variable 모델링을 향상시키기 위한 대체 분포 접근 방법에 대해 다룬다.
Nonparametric Prior for z
Non-parametric prior : Bayesian Nonparametrics에 속하는 Dirichlet processes 및 Indian Buffet Processes가 Bayesian 토픽 모델링에서 성공적으로 적용되어, 토픽의 수 (즉, K)를 자동으로 추론할 수 있게 해주는 방법